Difference between revisions of "Systems and Organizations"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
= Systems = | = Systems = | ||
is the wholistic function of organisation | |||
* Sales and marketing systems | |||
** order processing | |||
** market analysis | |||
** pricing analysis | |||
** sales and forecasting | |||
* Manufactuuring and production systems | |||
** Macnone control | |||
** Design (CAD) | |||
** production planning | |||
** Facilities location | |||
* Finance and accounting systems | |||
** Accounts | |||
** porfolio analysis | |||
** Budgetting | |||
** profit planning | |||
* human resource systems | |||
** Function responsible for attracting, developing and maintaining firm's work force | |||
** from strategic level to TPS | |||
Revision as of 22:50, 9 January 2010
Organisation
Definition
- Lewis H Haney: is a harmoneous adjustments of specialised parts for the accomplishment of common purpose
- Louis A Allen: process of identifying and grouping the work to be performed, defining and delegating the responsibility, establishing the relationship for the purpose of enabling the people to work most effectively together to accomplish the objectives
- Grouping of activities and resources in a logical fasion
Types
- Formal
- Structure of roles are formally organised
- Most effective in decision making, use of resources, focussed
- Informal
- Organisation that helps to accomplish the objectives in a indirect way
- Eg: Situational leadership, Playing chess during lunch hours
Benefits
- vision
- planning
- communication
- logical flow of work activities
- avoid conflict
- effective decision making
- Relationship
- focus
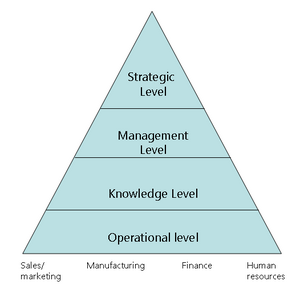
Information Flow in Organization
- Model information flow
- Operational level
- knowledge level
- management level
- Strategic level
- Types of Information System
- TPS: Transaction processing system
- at operational level
- computarised
- KWS: Knowledge work systems
- Office automation systems
- Documentation
- OAS: Office automation systems
- documents, schedules
- clerical
- MIS: Management Information System
- Integrated user-machine system for proving operations, support and decision making
- communication, coordination, control analysis and visualisation
- Characteristics
- serves at planning level
- works on existing data
- inflexible
- analytical and helps in decision making
- stable
- lengthy
- DSS: Decision support Systems
- uses: Decision making
- More sophisticated analysis
- provide users flexibility
- controls the whole process
- ESS: Executive support systems
- used by senior executives
- Decision making
- at strategic level
- TPS: Transaction processing system
- Characteristics of Information processing systems
Inputs Processing Outputs users ESS DSS MIS KWS OAS TPS
Systems
is the wholistic function of organisation
- Sales and marketing systems
- order processing
- market analysis
- pricing analysis
- sales and forecasting
- Manufactuuring and production systems
- Macnone control
- Design (CAD)
- production planning
- Facilities location
- Finance and accounting systems
- Accounts
- porfolio analysis
- Budgetting
- profit planning
- human resource systems
- Function responsible for attracting, developing and maintaining firm's work force
- from strategic level to TPS